The crypto 2.0 trade has been making robust progress up to now yr growing blockchain expertise, together with the formalization and in some circumstances realization of proof of stake designs like Slasher and DPOS, varied forms of scalable blockchain algorithms, blockchains utilizing “leader-free consensus” mechanisms derived from traditional Byzantine fault tolerance theory, in addition to financial substances like Schelling consensus schemes and stable currencies. All of those applied sciences treatment key deficiencies of the blockchain design with respect to centralized servers: scalability knocks down dimension limits and transaction prices, leader-free consensus reduces many types of exploitability, stronger PoS consensus algorithms cut back consensus prices and enhance safety, and Schelling consensus permits blockchains to be “conscious” of real-world information. Nevertheless, there’s one piece of the puzzle that each one approaches up to now haven’t but managed to crack: privateness.
Forex, Dapps and Privateness
Bitcoin brings to its customers a reasonably distinctive set of tradeoffs with respect to monetary privateness. Though Bitcoin does a considerably higher job than any system that got here earlier than it at defending the bodily identities behind every of its accounts – higher than fiat and banking infrastructure as a result of it requires no id registration, and higher than money as a result of it may be mixed with Tor to fully disguise bodily location, the presence of the Bitcoin blockchain implies that the precise transactions made by the accounts are extra public than ever – neither the US authorities, nor China, nor the 13 yr outdated hacker down the road even want a lot as a warrant with the intention to decide precisely which account despatched how a lot BTC to which vacation spot at what specific time. On the whole, these two forces pull Bitcoin in reverse instructions, and it’s not totally clear which one dominates.
With Ethereum, the scenario is analogous in concept, however in observe it’s reasonably totally different. Bitcoin is a blockchain meant for foreign money, and foreign money is inherently a really fungible factor. There exist strategies like merge avoidance which permit customers to basically faux to be 100 separate accounts, with their pockets managing the separation within the background. Coinjoin can be utilized to “combine” funds in a decentralized approach, and centralized mixers are an excellent choice too particularly if one chains a lot of them collectively. Ethereum, however, is meant to retailer intermediate state of any sort of processes or relationships, and sadly it’s the case that many processes or relationships which are considerably extra advanced than cash are inherently “account-based”, and huge prices could be incurred by attempting to obfuscate one’s actions by way of a number of accounts. Therefore, Ethereum, because it stands in the present day, will in lots of circumstances inherit the transparency facet of blockchain expertise far more so than the privateness facet (though these enthusiastic about utilizing Ethereum for foreign money can definitely construct higher-privacy money protocols within subcurrencies).
Now, the query is, what if there are circumstances the place folks really need privateness, however a Diaspora-style self-hosting-based resolution or a Zerocash-style zero-knowledge-proof technique is for no matter purpose inconceivable – for instance, as a result of we wish to carry out calculations that contain aggregating a number of customers’ personal information? Even when we clear up scalability and blockchain information belongings, will the dearth of privateness inherent to blockchains imply that we merely have to return to trusting centralized servers? Or can we give you a protocol that gives the very best of each worlds: a blockchain-like system which provides decentralized management not simply over the best to replace the state, however even over the best to entry the knowledge in any respect?
Because it seems, such a system is effectively inside the realm of risk, and was even conceptualized by Nick Szabo in 1998 underneath the moniker of “God protocols” (although, as Nick Szabo identified, we must always not use that time period for the protocols that we’re about to explain right here as God is mostly assumed and even defined to be Pareto-superior to every little thing else and as we’ll quickly see these protocols are very removed from that); however now with the arrival of Bitcoin-style cryptoeconomic expertise the event of such a protocol could for the primary time really be viable. What is that this protocol? To offer it a fairly technically correct however nonetheless comprehensible time period, we’ll name it a “secret sharing DAO”.
Fundamentals: Secret Sharing
To skip the enjoyable technical particulars and go straight to functions, click here
Secret computation networks depend on two elementary primitives to retailer data in a decentralized approach. The primary is secret sharing. Secret sharing basically permits information to be saved in a decentralized approach throughout N events such that any Ok events can work collectively to reconstruct the information, however Ok-1 events can not recuperate any data in any respect. N and Ok could be set to any values desired; all it takes is a number of easy parameter tweaks within the algorithm.
The best approach to mathematically describe secret sharing is as follows. We all know that two factors make a line:
So, to implement 2-of-N secret sharing, we take our secret S, generate a random slope m, and create the road y = mx + S. We then give the N events the factors on the road (1, m + S), (2, 2m + S), (3, 3m + S), and so on. Any two of them can reconstruct the road and recuperate the unique secret, however one particular person can do nothing; if you happen to obtain the purpose (4, 12), that may very well be from the road y = 2x + 4, or y = -10x + 52, or y = 305445x – 1221768. To implement 3-of-N secret sharing, we simply make a parabola as an alternative, and provides folks factors on the parabola:
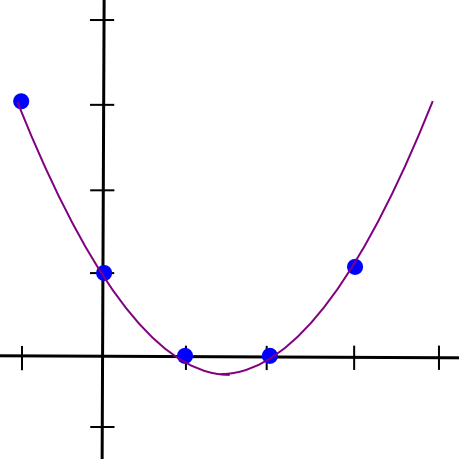
Parabolas have the property that any three factors on a parabola can be utilized to reconstruct the parabola (and nobody or two factors suffice), so basically the identical course of applies. And, extra usually, to implement Ok-of-N secret sharing, we use a level Ok-1 polynomial in the identical approach. There’s a set of algorithms for recovering the polynomial from a adequate set of factors in all such circumstances; they’re described in additional particulars in our earlier article on erasure coding.
That is how the key sharing DAO will retailer information. As a substitute of each taking part node within the consensus storing a duplicate of the complete system state, each taking part node within the consensus will retailer a set of shares of the state – factors on polynomials, one level on a distinct polynomial for every variable that makes up a part of the state.
Fundamentals: Computation
Now, how does the key sharing DAO do computation? For this, we use a set of algorithms referred to as secure multiparty computation (SMPC). The fundamental precept behind SMPC is that there exist methods to take information which is break up amongst N events utilizing secret sharing, carry out computations on it in a decentralized approach, and find yourself with the end result secret-shared between the events, all with out ever reconstituting any of the information on a single system.
SMPC with addition is simple. To see how, let’s return to the two-points-make-a-line instance, however now let’s have two traces:
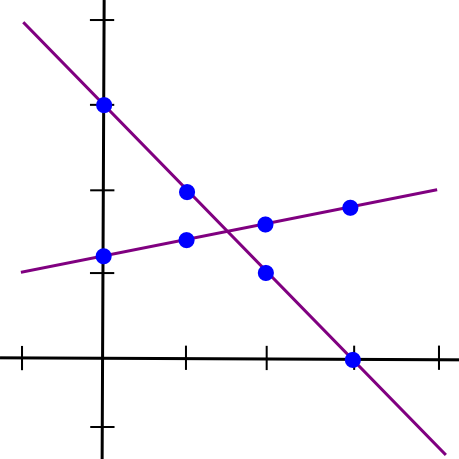
Suppose that the x=1 level of each traces A and B is saved by pc P[1], the x=2 level is saved by pc P[2], and so on. Now, suppose that P[1] computes a brand new worth, C(1) = A(1) + B(1), and B computes C(2) = A(2) + B(2). Now, let’s draw a line by means of these two factors:
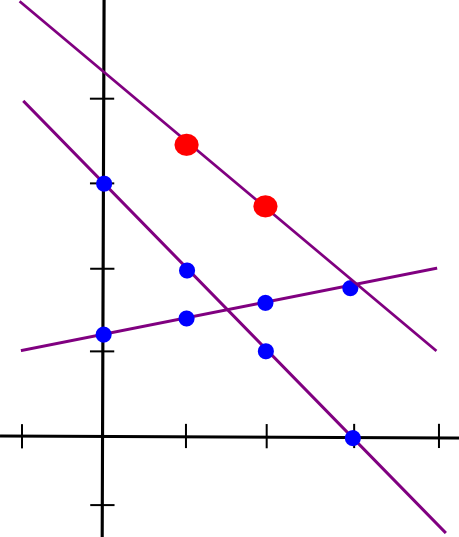
So now we have a brand new line, C, such that C = A + B at factors x=1 and x=2. Nevertheless, the fascinating factor is, this new line is definitely equal to A + B on each level:
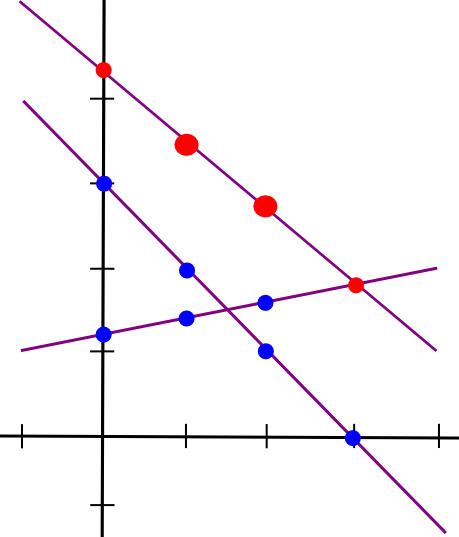
Thus, now we have a rule: sums of secret shares (on the similar x coordinate) are secret shares of the sum. Utilizing this precept (which additionally applies to greater dimensions), we will convert secret shares of a and secret shares of b into secret shares of a+b, all with out ever reconstituting a and b themselves. Multiplication by a identified fixed worth works the identical approach: okay instances the ith secret share of a is the same as the ith secret share of a*okay.
Multiplication of two secret shared values, sadly, is much more involved. The method will take a number of steps to clarify, and since it’s pretty difficult in any case it is price merely doing for arbitrary polynomials straight away. Here is the magic. First, suppose that there exist values a and b, secret shared amongst events P[1] … P[n], the place a[i] represents the ith share of a (and similar for b[i] and b). We begin off like this:
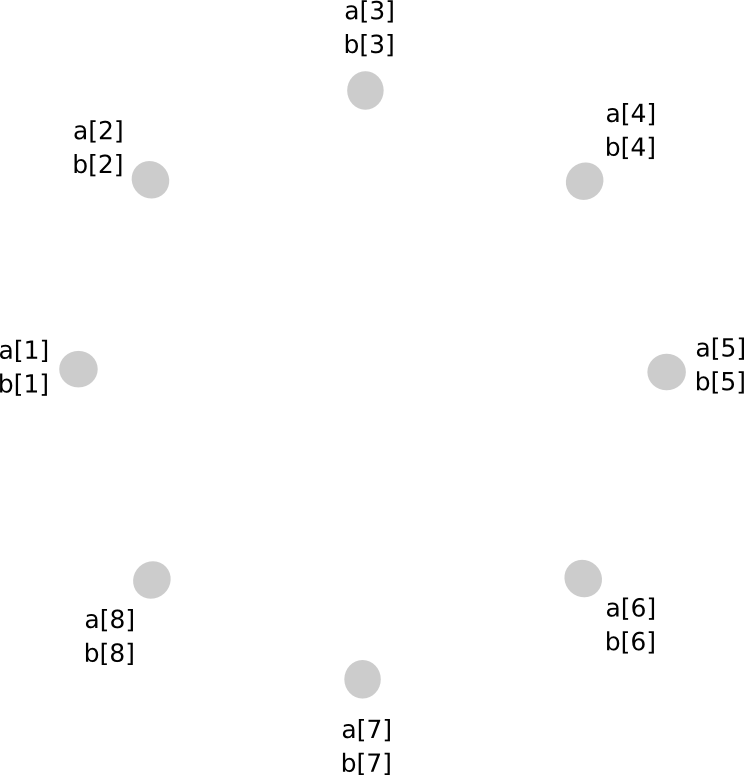
Now, one choice that you simply would possibly consider is, if we will simply make a brand new polynomial c = a + b by having each occasion retailer c[i] = a[i] + b[i], cannot we do the identical for multiplication as effectively? The reply is, surprisingly, sure, however with a major problem: the brand new polynomial has a level twice as massive as the unique. For instance, if the unique polynomials had been y = x + 5 and y = 2x – 3, the product could be y = 2x^2 + 7x – 15. Therefore, if we do multiplication greater than as soon as, the polynomial would turn into too huge for the group of N to retailer.
To keep away from this downside, we carry out a kind of rebasing protocol the place we convert the shares of the bigger polynomial into shares of a polynomial of the unique diploma. The way in which it really works is as follows. First, occasion P[i] generates a brand new random polynomial, of the identical diploma as a and b, which evaluates to c[i] = a[i]*b[i] at zero, and distributes factors alongside that polynomial (ie. shares of c[i]) to all events.
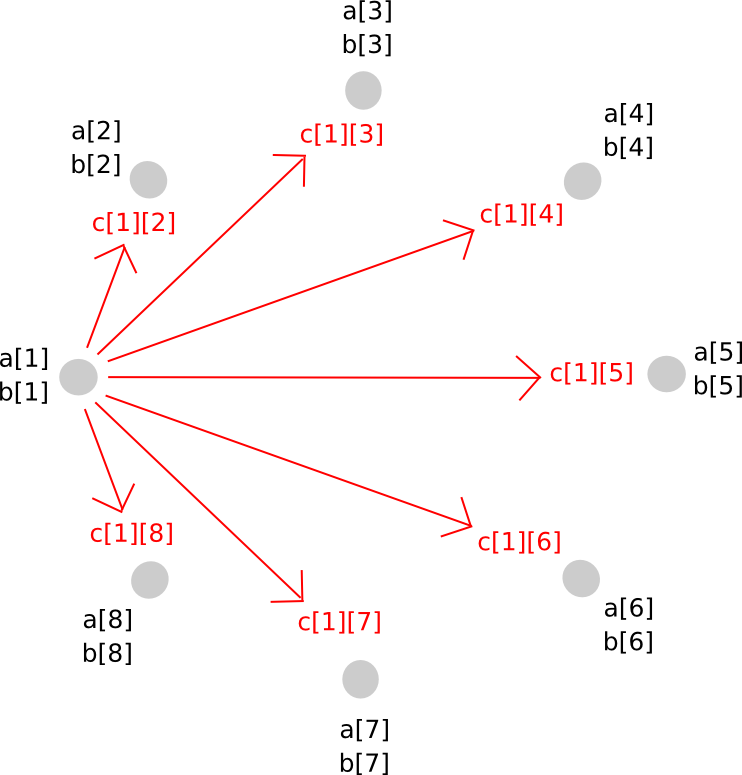
Thus, P[j] now has c[i][j] for all i. Given this, P[j] calculates c[j], and so everybody has secret shares of c, on a polynomial with the identical diploma as a and b.
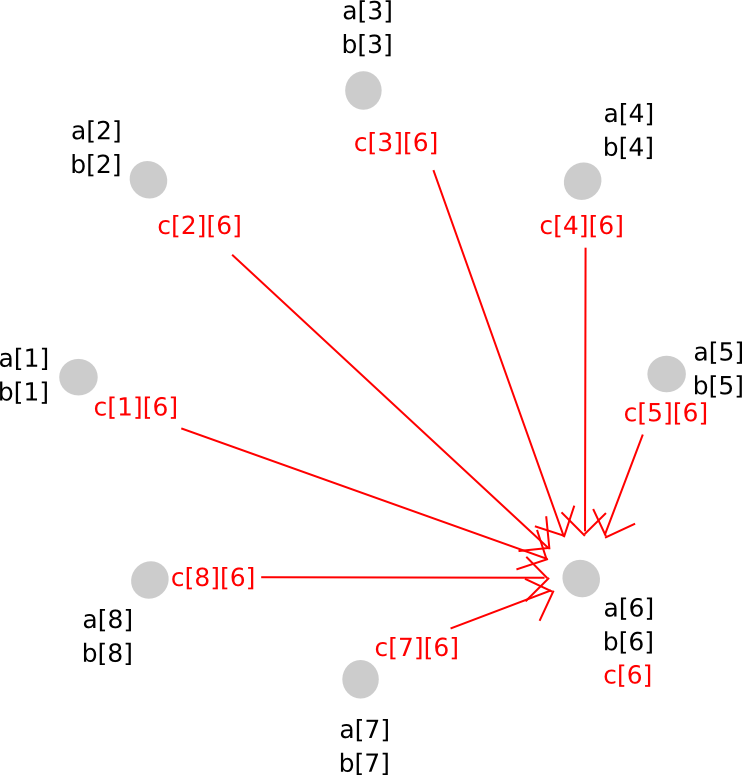
To do that, we used a intelligent trick of secret sharing: as a result of the key sharing math itself entails nothing greater than additions and multiplications by identified constants, the 2 layers of secret sharing are commutative: if we apply secret sharing layer A after which layer B, then we will take layer A off first and nonetheless be protected by layer B. This enables us to maneuver from a higher-degree polynomial to a decrease diploma polynomial however keep away from revealing the values within the center – as an alternative, the center step concerned each layers being utilized on the similar time.
With addition and multiplication over 0 and 1, now we have the power to run arbitrary circuits within the SMPC mechanism. We are able to outline:
- AND(a, b) = a * b
- OR(a, b) = a + b – a * b
- XOR(a, b) = a + b – 2 * a * b
- NOT(a) = 1 – a
Therefore, we will run no matter applications we wish, though with one key limitation: we will not do secret conditional branching. That’s, if we had a computation if (x == 5)
There are two methods round this downside. First, we will use multiplication as a “poor man’s if” – exchange one thing like if (x == 5)
The key-sharing primarily based protocol described above is just one approach to do comparatively merely SMPC; there are different approaches, and to attain safety there’s additionally a necessity so as to add a verifiable secret sharing layer on high, however that’s past the scope of this text – the above description is just meant to indicate how a minimal implementation is feasible.
Constructing a Forex
Now that now we have a tough concept of how SMPC works, how would we use it to construct a decentralized foreign money engine? The final approach {that a} blockchain is normally described on this weblog is as a system that maintains a state, S, accepts transactions, agrees on which transactions ought to be processed at a given time and computes a state transition perform APPLY(S, TX) -> S’ OR INVALID. Right here, we are going to say that all transactions are legitimate, and if a transaction TX is invalid then we merely have APPLY(S, TX) = S.
Now, because the blockchain will not be clear, we would count on the necessity for 2 sorts of transactions that customers can ship into the SMPC: get requests, asking for some particular details about an account within the present state, and replace requests, containing transactions to use onto the state. We’ll implement the rule that every account can solely ask for steadiness and nonce details about itself, and might withdraw solely from itself. We outline the 2 kinds of requests as follows:
SEND: [from_pubkey, from_id, to, value, nonce, sig] GET: [from_pubkey, from_id, sig]
The database is saved among the many N nodes within the following format:
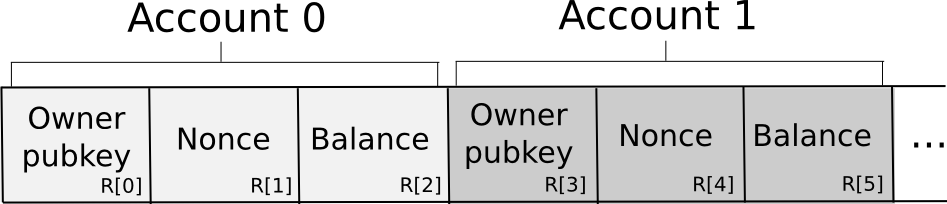
Primarily, the database is saved as a set of 3-tuples representing accounts, the place every 3-tuple shops the proudly owning pubkey, nonce and steadiness. To ship a request, a node constructs the transaction, splits it off into secret shares, generates a random request ID and attaches the ID and a small quantity of proof of labor to every share. The proof of labor is there as a result of some anti-spam mechanism is important, and since account balances are personal there is no such thing as a approach if the sending account has sufficient funds to pay a transaction payment. The nodes then independently confirm the shares of the signature in opposition to the share of the general public key provided within the transaction (there are signature algorithms that assist you to do this sort of per-share verification; Schnorr signatures are one main class). If a given node sees an invalid share (attributable to proof of labor or the signature), it rejects it; in any other case, it accepts it.
Transactions which are accepted will not be processed instantly, very similar to in a blockchain structure; at first, they’re saved in a reminiscence pool. On the finish of each 12 seconds, we use some consensus algorithm – it may very well be one thing easy, like a random node from the N deciding as a dictator, or a complicated neo-BFT algorithm like that utilized by Pebble – to agree on which set of request IDs to course of and by which order (for simplicity, easy alphabetical order will most likely suffice).
Now, to fufill a GET request, the SMPC will compute and reconstitute the output of the next computation:
owner_pubkey = R[0] * (from_id == 0) + R[3] * (from_id == 1) + ... + R[3*n] * (from_id == n) legitimate = (owner_pubkey == from_pubkey) output = legitimate * (R[2] * (from_id == 0) + R[5] * (from_id == 1) + ... + R[3n + 2] * (from_id == n))
So what does this components do? It consists of three levels. First, we extract the proprietor pubkey of the account that the request is attempting to get the steadiness of. As a result of the computation is finished within an SMPC, and so no node really is aware of what database index to entry, we do that by merely taking all of the database indices, multiplying the irrelevant ones by zero and taking the sum. Then, we test if the request is attempting to get information from an account which is definitely owns (keep in mind that we checked the validity of from_pubkey in opposition to the signature in step one, so right here we simply have to test the account ID in opposition to the from_pubkey). Lastly, we use the identical database getting primitive to get the steadiness, and multiply the steadiness by the validity to get the end result (ie. invalid requests return a steadiness of 0, legitimate ones return the precise steadiness).
Now, let’s take a look at the execution of a SEND. First, we compute the validity predicate, consisting of checking that (1) the general public key of the focused account is right, (2) the nonce is right, and (3) the account has sufficient funds to ship. Word that to do that we as soon as once more want to make use of the “multiply by an equality test and add” protocol, however for brevity we are going to abbreviate R[0] * (x == 0) + R[3] * (x == 1) + … with R[x * 3].
legitimate = (R[from_id * 3] == from_pubkey) * (R[from_id * 3 + 1] == nonce) * (R[from_id * 3 + 2] >= worth)
We then do:
R[from_id * 3 + 2] -= worth * legitimate R[from_id * 3 + 1] += legitimate R[to * 3 + 2] += worth * legitimate
For updating the database, R[x * 3] += y expands to the set of directions R[0] += y * (x == 0), R[3] += y * (x == 1) …. Word that each one of those could be parallelized. Additionally, notice that to implement steadiness checking we used the >= operator. That is as soon as once more trivial utilizing boolean logic gates, however even when we use a finite discipline for effectivity there do exist some clever tricks for performing the test utilizing nothing however additions and multiplications.
In all the above we noticed two elementary limitations in effectivity within the SMPC structure. First, studying and writing to a database has an O(n) price as you just about must learn and write each cell. Doing something much less would imply exposing to particular person nodes which subset of the database a learn or write was from, opening up the potential of statistical reminiscence leaks. Second, each multiplication requires a community message, so the basic bottleneck right here will not be computation or reminiscence however latency. Due to this, we will already see that secret sharing networks are sadly not God protocols; they’ll do enterprise logic simply wonderful, however they may by no means have the ability to do something extra difficult – even crypto verifications, except a choose few crypto verifications particularly tailor-made to the platform, are in lots of circumstances too costly.
From Forex to EVM
Now, the subsequent downside is, how can we go from this easy toy foreign money to a generic EVM processor? Nicely, allow us to study the code for the digital machine inside a single transaction setting. A simplified model of the perform appears to be like roughly as follows:
def run_evm(block, tx, msg, code): computer = 0 fuel = msg.fuel stack = [] stack_size = 0 exit = 0 whereas 1: op = code[pc] fuel -= 1 if fuel 0 or stack_size get_stack_req(op): exit = 1 if op == ADD: x = stack[stack_size] y = stack[stack_size - 1] stack[stack_size - 1] = x + y stack_size -= 1 if op == SUB: x = stack[stack_size] y = stack[stack_size - 1] stack[stack_size - 1] = x - y stack_size -= 1 ... if op == JUMP: computer = stack[stack_size] stack_size -= 1 ...
The variables concerned are:
- The code
- The stack
- The reminiscence
- The account state
- This system counter
Therefore, we will merely retailer these as information, and for each computational step run a perform just like the next:
op = code[pc] * alive + 256 * (1 - alive) fuel -= 1 stack_p1[0] = 0 stack_p0[0] = 0 stack_n1[0] = stack[stack_size] + stack[stack_size - 1] stack_sz[0] = stack_size - 1 new_pc[0] = computer + 1 stack_p1[1] = 0 stack_p0[1] = 0 stack_n1[1] = stack[stack_size] - stack[stack_size - 1] stack_sz[1] = stack_size - 1 new_pc[1] = computer + 1 ... stack_p1[86] = 0 stack_p0[86] = 0 stack_n1[86] = stack[stack_size - 1] stack_sz[86] = stack_size - 1 new_pc[86] = stack[stack_size] ... stack_p1[256] = 0 stack_p0[256] = 0 stack_n1[256] = 0 stack_sz[256] = 0 new_pc[256] = 0 computer = new_pc[op] stack[stack_size + 1] = stack_p1[op] stack[stack_size] = stack_p0[op] stack[stack_size - 1] = stack_n1[op] stack_size = stack_sz[op] computer = new_pc[op] alive *= (fuel 0) * (stack_size 0)
Primarily, we compute the results of each single opcode in parallel, after which choose the right one to replace the state. The alive variable begins off at 1, and if the alive variable at any level switches to zero, then all operations from that time merely do nothing. This appears horrendously inefficient, and it’s, however keep in mind: the bottleneck will not be computation time however latency. Every little thing above could be parallelized. Actually, the astute reader could even discover that all the means of operating each opcode in parallel has solely O(n) complexity within the variety of opcodes (significantly if you happen to pre-grab the highest few objects of the stack into specified variables for enter in addition to output, which we didn’t do for brevity), so it’s not even probably the most computationally intensive half (if there are extra accounts or storage slots than opcodes, which appears probably, the database updates are). On the finish of each N steps (or for even much less data leakage each energy of two of steps) we reconstitute the alive variable and if we see that alive = 0 then we halt.
In an EVM with many members, the database will probably be the most important overhead. To mitigate this downside, there are probably intelligent data leakage tradeoffs that may be made. For instance, we already know that more often than not code is learn from sequential database indices. Therefore, one method could be to retailer the code as a sequence of huge numbers, every massive quantity encoding many opcodes, after which use bit decomposition protocols to learn off particular person opcodes from a quantity as soon as we load it. There are additionally probably some ways to make the digital machine essentially far more environment friendly; the above is supposed, as soon as once more, as a proof of idea to indicate how a secret sharing DAO is essentially potential, not something near an optimum implementation. Moreover, we will look into architectures just like those utilized in scalability 2.0 techniques to extremely compartmentalize the state to additional improve effectivity.
Updating the N
The SMPC mechanism described above assumes an current N events concerned, and goals to be safe in opposition to any minority of them (or in some designs at the least any minority lower than 1/4 or 1/3) colluding. Nevertheless, blockchain protocols have to theoretically final perpetually, and so stagnant financial units don’t work; reasonably, we have to choose the consensus members utilizing some mechanism like proof of stake. To do that, an instance protocol would work as follows:
- The key sharing DAO’s time is split into “epochs”, every maybe someplace between an hour and every week lengthy.
- Throughout the first epoch, the members are set to be the highest N members throughout the genesis sale.
- On the finish of an epoch, anybody has the power to enroll to be one of many members within the subsequent spherical by placing down a deposit. N members are randomly chosen, and revealed.
- A “decentralized handoff protocol” is carried out, the place the N members concurrently break up their shares among the many new N, and every of the brand new N reconstitutes their share from the items that they acquired – basically, the very same protocol as was used for multiplication. Word that this protocol can be used to extend or lower the variety of members.
All the above handles decentralization assuming trustworthy members; however in a cryptocurrency protocol we additionally want incentives. To perform that, we use a set of primitives referred to as verifiable secret sharing, that enable us to find out whether or not a given node was performing truthfully all through the key sharing course of. Primarily, this course of works by doing the key sharing math in parallel on two totally different ranges: utilizing integers, and utilizing elliptic curve factors (different constructions additionally exist, however as a result of cryptocurrency customers are most aware of the secp256k1 elliptic curve we’ll use that). Elliptic curve factors are handy as a result of they’ve a commutative and associative addition operator – in essence, they’re magic objects which could be added and subtracted very similar to numbers can. You’ll be able to convert a quantity into a degree, however not a degree right into a quantity, and now we have the property that number_to_point(A + B) = number_to_point(A) + number_to_point(B). By doing the key sharing math on the quantity degree and the elliptic curve level degree on the similar time, and publicizing the elliptic curve factors, it turns into potential to confirm malfeasance. For effectivity, we will most likely use a Schellingcoin-style protocol to permit nodes to punish different nodes which are malfeasant.
Purposes
So, what do now we have? If the blockchain is a decentralized pc, a secret sharing DAO is a decentralized pc with privateness. The key sharing DAO pays dearly for this further property: a community message is required per multiplication and per database entry. In consequence, fuel prices are prone to be a lot greater than Ethereum correct, limiting the computation to solely comparatively easy enterprise logic, and barring using most sorts of cryptographic calculations. Scalability expertise could also be used to partially offset this weak spot, however in the end there’s a restrict to how far you will get. Therefore, this expertise will most likely not be used for each use case; as an alternative, it can function extra like a special-purpose kernel that may solely be employed for particular sorts of decentralized functions. Some examples embrace:
- Medical information – preserving the information on a non-public decentralized platform can doubtlessly open the door for an easy-to-use and safe well being data system that retains sufferers answerable for their information. Notably, notice that proprietary analysis algorithms might run inside the key sharing DAO, permitting medical analysis as a service primarily based on information from separate medical checkup companies with out operating the chance that they may deliberately or unintentionally expose your personal particulars to insurers, advertisers or different companies.
- Personal key escrow – a decentralized M-of-N various to centralized password restoration; may very well be used for monetary or non-financial functions
- Multisig for something – even techniques that don’t natively assist arbitrary entry insurance policies, and even M-of-N multisignature entry, now will, since so long as they assist cryptography you’ll be able to stick the personal key within a secret sharing DAO.
- Repute techniques – what if repute scores had been saved inside a secret sharing DAO so you can privately assign repute to different customers, and have your project depend in direction of the entire repute of that consumer, with out anybody having the ability to see your particular person assignments?
- Personal monetary techniques – secret sharing DAOs might present another path to Zerocash-style totally nameless foreign money, besides that right here the performance may very well be far more simply prolonged to decentralized trade and extra advanced sensible contracts. Enterprise customers could wish to leverage a few of the advantages of operating their firm on high of crypto with out essentially exposing each single one among their inner enterprise processes to most of the people.
- Matchmaking algorithms – discover employers, staff, relationship companions, drivers on your subsequent trip on Decentralized Uber, and so on, however doing the matchmaking algorithm computations within SMPC in order that nobody sees any details about you except the algorithm determines that you’re a excellent match.
Primarily, one can consider SMPC as providing a set of instruments roughly just like that which it has been theorized could be supplied by cryptographically secure code obfuscation, besides with one key distinction: it really works on human-practical time scales.
Additional Penalties
Except for the functions above, what else will secret sharing DAOs convey? Notably, is there something to fret about? Because it seems, identical to with blockchains themselves, there are a number of issues. The primary, and most evident, challenge is that secret sharing DAOs will considerably improve the scope of functions that may be carried out in a very personal style. Many advocates of blockchain expertise typically base a big a part of their argument on the important thing level that whereas blockchain-based currencies provide an unprecedented quantity of anonymity within the sense of not linking addresses to particular person identities, they’re on the similar time probably the most public type of foreign money on the earth as a result of each transaction is situated on a shared ledger. Right here, nevertheless, the primary half stays, however the second half disappears fully. What now we have left is basically whole anonymity.
If it seems to be the case that this degree of anonymity permits for a a lot greater diploma of felony exercise, and the general public will not be proud of the tradeoff that the expertise brings, then we will predict that governments and different establishments basically, even perhaps alongside volunteer vigilante hackers, will attempt their greatest to take these techniques down, and maybe they’d even be justified. Thankfully for these attackers, nevertheless, secret sharing DAOs do have an inevitable backdoor: the 51% assault. If 51% of the maintainers of a secret sharing DAO at some specific time determine to collude, then they’ll uncover any of the information that’s underneath their supervision. Moreover, this energy has no statute of limitations: if a set of entities who fashioned over half of the sustaining set of a secret sharing DAO in some unspecified time in the future a few years in the past collude, then even then the group would have the ability to unearth the knowledge from that cut-off date. Briefly, if society is overwhelmingly against one thing being performed within a secret sharing DAO, there shall be loads of alternative for the operators to collude to cease or reveal what is going on on.
A second, and subtler, challenge is that the idea of secret sharing DAOs drives a stake by means of a cherished truth of cryptoeconomics: that personal keys will not be securely tradeable. Many protocols explicitly, or implicitly, depend on this concept, together with non-outsourceable proof of work puzzles, Vlad Zamfir and Pavel Kravchenko’s proof of custody, financial protocols that use personal keys as identities, any sort of financial standing that goals to be untradeable, and so on. On-line voting techniques typically have the requirement that it ought to be inconceivable to show that you simply voted with a specific key, in order to stop vote promoting; with secret sharing DAOs, the issue is that now you really can promote your vote, reasonably merely: by placing your personal key right into a contract within a secret sharing DAO, and renting out entry.
The implications of this capacity to promote personal keys are fairly far reaching – actually, they go as far as to nearly threaten the safety of the strongest out there system underlying blockchain safety: proof of stake. The potential concern is that this: proof of stake derives its safety from the truth that customers have safety deposits on the blockchain, and these deposits can doubtlessly be taken away if the consumer misacts in some style (double-voting, voting for a fork, not voting in any respect, and so on). Right here, personal keys turn into tradeable, and so safety deposits turn into tradeable as effectively. We should ask the query: does this compromise proof of stake?
Thankfully, the reply is not any. Initially, there are robust lemon-theoretic arguments for why nobody would really need to promote their deposit. When you have a deposit of $10, to you that is price $10 minus the tiny chance that you’ll get hacked. However if you happen to attempt to promote that deposit to another person, they may have a deposit which is price $10, except you determine to make use of your personal key to double-vote and thus destroy the deposit. Therefore, from their standpoint, there’s a fixed overhanging danger that you’ll act to take their deposit away, and also you personally haven’t any incentive not to do this. The actual fact that you’re attempting to unload your deposit ought to make them suspicious. Therefore, from their standpoint, your deposit would possibly solely be price, say, $8. You don’t have any purpose to sacrifice $10 for $8, in order a rational actor you’ll maintain the deposit to your self.
Second, if the personal key was within the secret sharing DAO proper from the beginning, then by transferring entry to the important thing you’ll personally lose entry to it, so you’ll really switch the authority and the legal responsibility on the similar time – from an financial standpoint, the impact on the system could be precisely the identical as if one of many deposit holders merely had a change of persona in some unspecified time in the future throughout the course of. Actually, secret sharing DAOs could even enhance proof of stake, by offering a safer platform for customers to take part in decentralized stake swimming pools even in protocols like Tendermint, which don’t natively assist such performance.
There are additionally different explanation why the theoretical assaults that secret sharing DAOs make potential could actually fail in observe. To take one instance, take into account the case of non-outsourceable puzzles, computational issues which attempt to show possession of a non-public key and a chunk of knowledge on the similar time. One sort of implementation of a non-outsourceable puzzle, utilized by Permacoin, entails a computation which must “bounce” backwards and forwards between the important thing and the information a whole bunch of hundreds of instances. That is simple to do you probably have the 2 items of knowledge on the identical piece of {hardware}, however turns into prohibitively sluggish if the 2 are separated by a community connection – and over a secret sharing DAO it will be practically inconceivable because of the inefficiencies. In consequence, one potential conclusion of all that is that secret sharing DAOs will result in the standardization of a signature scheme which requires a number of hundred hundreds of thousands of rounds of computation – ideally with tons and plenty of serial multiplication – to compute, at which level each pc, cellphone or internet-of-things microchip would have a built-in ASIC to do it trivially, secret sharing DAOs could be left within the mud, and we might all transfer on with our lives.
How Far Away?
So what’s left earlier than secret sharing DAO expertise can go mainstream? Briefly, fairly a bit, however not an excessive amount of. At first, there’s definitely a reasonable quantity of technical engineering concerned, at the least on the protocol degree. Somebody must formalize an SMPC implementation, along with how it will be mixed with an EVM implementation, most likely with many restrictions for effectivity (eg. hash features within SMPC are very costly, so Merkle tree storage could disappear in favor of each contract having a finite variety of storage slots), a punishment, incentive and consensus framework and a hypercube-style scalability framework, after which launch the protocol specification. From that time, it is a number of months of growth in Python (Python ought to be wonderful, as by far the first bottleneck shall be community latency, not computation), and we’ll have a working proof of idea.
Secret sharing and SMPC expertise has been on the market for a few years, and tutorial cryptographers have been speaking about find out how to construct privacy-preserving functions utilizing M-of-N-based primitives and associated applied sciences similar to personal data retrieval for over a decade. The important thing contribution made by Bitcoin, nevertheless, is the concept M-of-N frameworks basically could be far more simply bootstrapped if we add in an financial layer. A secret sharing DAO with a foreign money inbuilt would offer incentives for people to take part in sustaining the community, and would bootstrap it till the purpose the place it may very well be totally self-sustaining on inner functions. Thus, altogether, this expertise is sort of potential, and never practically so far-off; it’s only a matter of time till somebody does it.
